Justin Moll
Director of Marketing
VadaTech, Inc.
702-896-3337
www.vadatech.com
MicroTCA is an open-standard embedded computing architecture developed by the PCI Industrial Computer Manufacturer’s Group (PICMG). The technology offers tremendous performance in a small form factor. The design of the systems provides inherent EMI protection for all types of designs and applications. MicroTCA also provides significant benefits of system management, redundancy options, high-speed, flexible serial protocols, rugged industrial or mil/aero design, and more. High-energy physics applications are specifically addressed by the MicroTCA.4 specification.
About MicroTCA
With its versatile design, MicroTCA is used in a wide range of applications. This includes telecommunications, military/aerospace, enterprise networking, industrial automation, medical, transportation, energy, and more. Here are some advantages over other open architectures:
- Fully redundant (not a single point of failure exists in the architecture)
– 99.99999 up time expected
- Hot swappable modules
- Serial bus
- High speed fabric interface up to 10Gb per lane
- Clocks
- Chassis management
- Vertical market
The form factor uses modules of approximately 75mm x 3HP (to 6HP) x 180mm deep boards plugging into 19” rackmount or smaller bench-top chassis. There are also double sized boards and various configurations for a versatile, compact architecture.
By configuring highly diverse collections of Advanced Mezzanine Cards (AMCs) in a modular MicroTCA Shelf, many different application architectures can be easily realized. The AMCs plug into the chassis and come in various types with functions such as processing, networking, graphics, storage, shelf management, and more. The common elements defined by MicroTCA are capable of interconnecting these AdvancedMCs in many interesting ways—powering and managing them, all at high efficiency and low cost. The flexibility of protocols includes:
- AMC.0 base specification
- AMC.1 PCIe
- AMC.2 GbE and 10GbE
- AMC.3 SAS/SATA
- AMC.4 Serial RapidIO
Module Gasketing
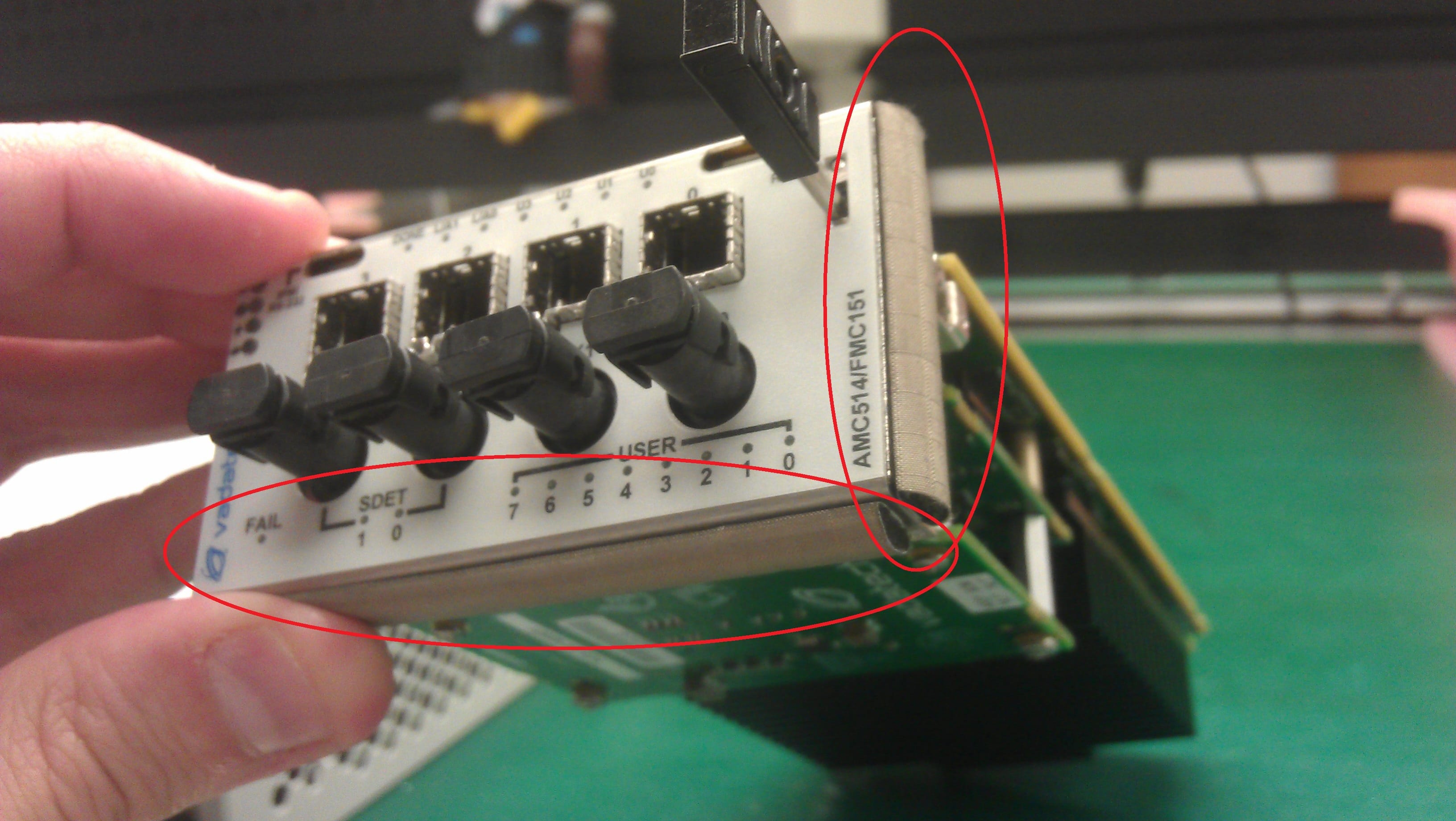
The pluggable AMC modules utilize a core foam sleeve with textile cladding that has a CuNi coating. The sleeve has a rounded isosceles triangle-like shape. The formable gasket is flexible enough to provide a solid seal with the enclosure. All AMCs have similar gasketing for consistency in EMC performance across various vendors’ product lines. The side of the AMC has similar gasketing on one edge of the board. Gasketing is not required on all sides as the shape of the gasket creates enough force for a solid seal. Further, the shape of the gasket covers the top area of the top of the AMC panel block, so there is a significant area that aids in containment. See Fig 1.
EMC Requirements for MicroTCA
The following is a brief excerpt of the EMC requirements from the MicroTCA.0 specification:
“All MicroTCA equipment shall meet Class A limits and should meet Class B limits of the following regulatory standards/requirements:
For ITE equipment in Europe: EN 55022 and EN 55024 (equivalent to CISPR22 and CISPR24 used in most countries)
For CO equipment in Europe: EN 300 386, Electro-Magnetic Compatibility (EMC) Requirements for Public Telecommunication Network Equipment, Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Requirements (similar to EN 55022 and EN55024 combined).
For USA: FCC CFR 47 Part 15, Subpart B”*
Thus, MicroTCA utilizes established and proven Telecom and other standards for EMC, ensuring reliability.
EMC Testing
EMC Testing of initial MicroTCA chassis are performed to IEC TS 61587-3 (2 GHz). The frequency range is 30 MHz to 3 000 MHz, with the attenuation values chosen for the definition of the shielding performance level of cabinets and subracks for the IEC 60297 and IEC 60917.
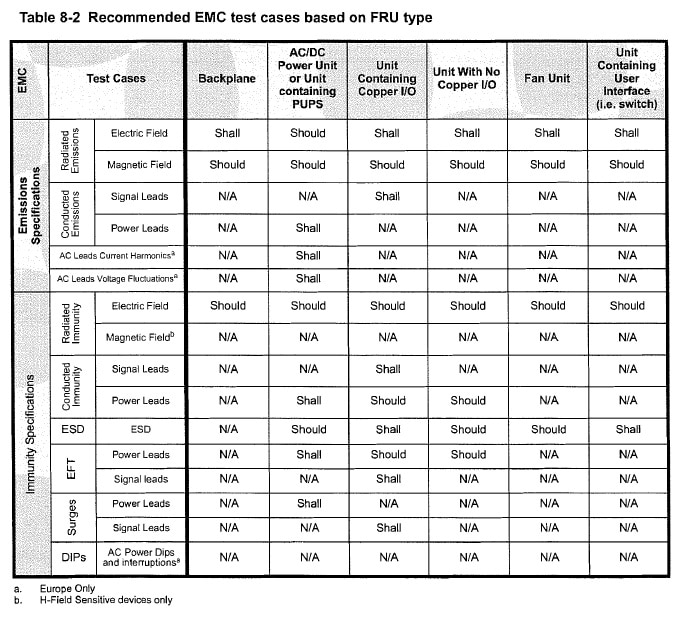
System-level testing is another important aspect of the specification. Regulatory EMC requirements call for compliance at the system level. Therefore, claiming conformance at the FRU (Field Replaceable Unit) level is not accepted (except for PC peripherals in some jurisdictions). Testing has to be done at the fully-loaded system level (representative worst case). The table below shows the recommended test cases based on the FRU type. See Fig 3*.
Chassis Gasketing
The MicroTCA chassis comes in several sizes and form factors. The most common are horizontal-mount chassis, often in 1U-3U heights. Even in a 1U height, a MicroTCA chassis can hold up to 12 AMCs, offering tremendous performance in a small space. The enclosures also come in vertical mount orientations, typically from 4U to 8U high. These can hold standard 75mm wide (tall in this case) boards or double width sized at approximately 150mm.
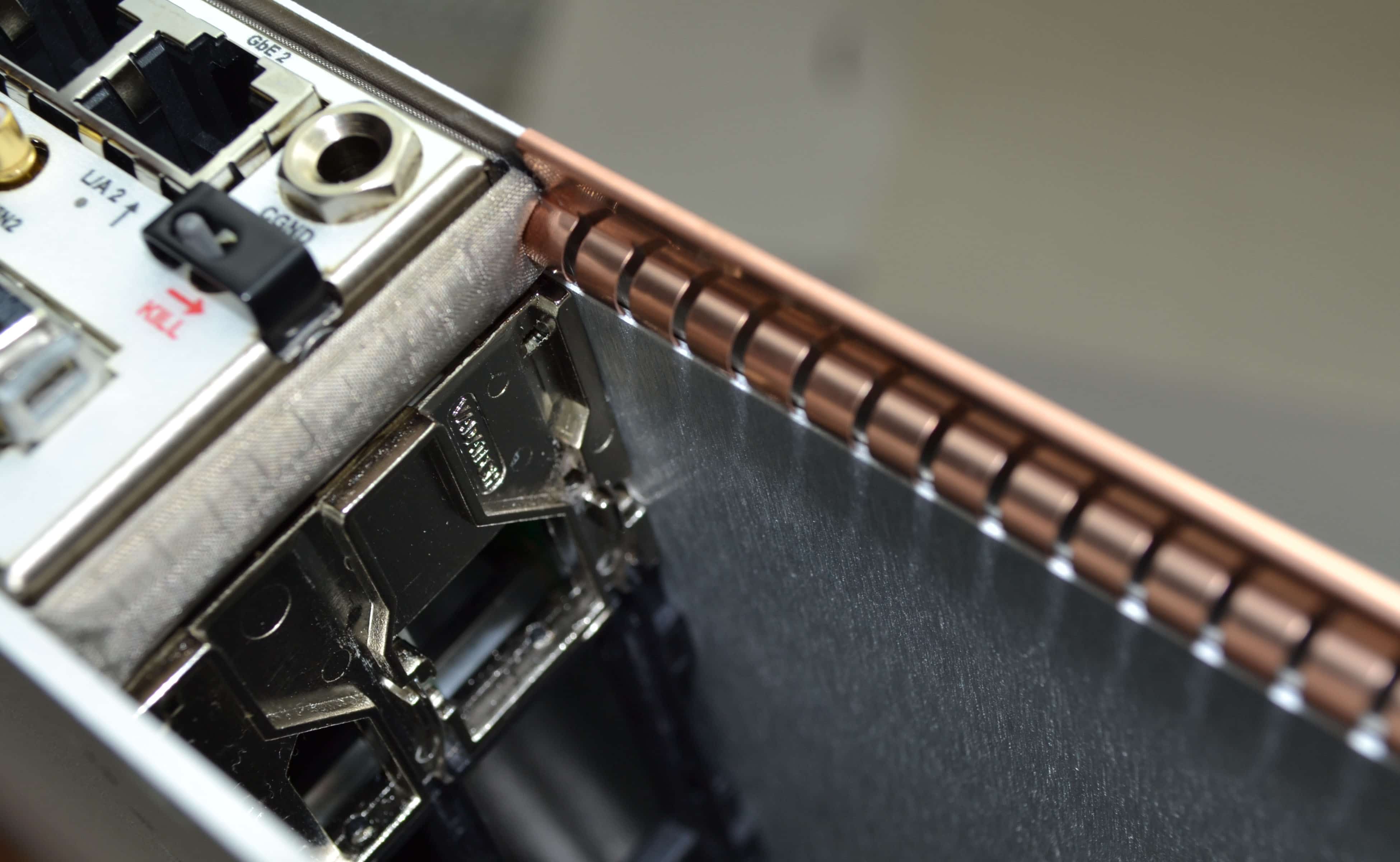
Often, the AMCs provide enough shielding in those areas of the chassis. See Fig 2 of a MicroTCA chassis with very simple additional gasketing. But, additional gasketing may be required, which is easily implemented. Aside from the various types of boards that plug in, there are also Cooling Units (often redundant push-pull) that may require gasketing depending on the solution provided by the vendor.
High Performance, Inherent EMC
MicroTCA provides a scalable, powerful, compact, and versatile platform for all types of computing applications. Utilizing proven EMC techniques, the shielding performance of the specification is built-in to the architecture. This decreases the engineers risk and help to ensure more consistent performance. PICMG also provides an online short-form specification for those interested in the background of the technology.
*excerpt from PICMG® MTCA.0 Micro Telecommunications Computing Architecture (MicroTCA.0) specification.