As we progress through the fold of technological developments, be it in commercial products, military advancements, automotive electronics, or any of the other industries where electromagnetic devices are developed, EMI will be present and EMC testing will be required. For those technical personnel who are walking into a laboratory for the first time, learning EMC because … [Read more...]
Filter Installation Issues: Input and Output Conductors
Real-life filter performance is totally dependant on how they are installed, especially on the impedance of the RF Reference and the impedance of the method used to electrically bond the filter to its RF Reference. Not only should these impedances be much lower than that of the shunt capacitors in the filters, they should also allow the internal and external CM surface currents … [Read more...]
5 Ways to Eliminate Ground Loops — Part 1
A Brief Introduction Most workers already know that proper grounding is a fundamental safety precaution for all kinds of electrical equipment. However, it’s less well known that while grounding can prevent and resolve many safety and power issues, improper grounding can create problems in data logging, data acquisition, and measurement and control systems. One of the most … [Read more...]
Designing and Selecting Filters: Using Soft Ferrite Cores
All inductors (L) suffer from RF resonances, and are only effective in filters at frequencies not far above their first (parallel) resonance (see section 1.8.1 of [7]). But so-called ‘soft ferrites’ behave resistively at RF, and the resulting lack of RF resonances helps make filters that use them have better and more predictable performance at RF. For example, a typical small … [Read more...]
Designing and Selecting Filters: Maximizing Impedance Discontinuities
To design effective filters we must maximize impedance discontinuities, at the frequencies of concern for emissions and/or immunity. Capacitors are used in conjunction with the RF Reference Plane (see Figure 1) to create low impedances, applied in shunt, whilst resistors or inductors are used to create high impedances, applied in series. When the source and … [Read more...]
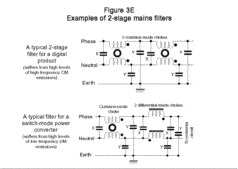
Designing and Selecting Filters: Differential Mode and Common Mode
Differential-mode (DM) and Common-mode (CM) Wanted signals are always DM: they flow along the ‘send’ conductor, and flow back along the ‘return’ conductor(s). In single-ended signalling, all the return currents share a common conducting structure, usually the 0V of the DC power distribution system. In balanced (or ‘differential’) signalling there is a dedicated conductor for … [Read more...]
Designing and Selecting Filters: The Importance of RF Reference
The Importance of the RF Reference The RF Reference is the node on a circuit’s schematic that we define as our reference voltage when designing an RF circuit or measuring its performance. For the most cost-effective EMC, all circuits (digital, analogue, switch-mode, etc.) should now be designed using RF techniques. It is common practice to call the RF Reference ‘earth’ or … [Read more...]
Designing and Selecting Filters: How Filters Work
Ignoring all the poles and zeroes in the filter textbooks: filters work by creating an intentional discontinuity in the characteristic impedance of a current path, reflecting radio frequency (RF) energy away from a protected circuit, or absorbing the RF energy (converting it to heat) – rather like a shield does, as will be described in Part 4 of this series. The greater the … [Read more...]
What is an EMC Risk Analysis?
Introduction The European EMC Directive (2014/30/EU) was updated in 2014, replacing the old directive (2008/108/EC) and became mandatory from April 2016 for any new product entering the EU from that date onwards. The change of directive was aimed at aligning the wording and terminology to ensure it was consistent with other CE Marking directives and implement standard text … [Read more...]
Cost-Effective Applications of EMI Gaskets
Introduction EMI gaskets are used extensively by the electrical/electronic industry to assist in complying with the various EMI radiated emission requirements. These requirements include compliance to DoD TEMPEST and EMI, and FCC and EU EMI test limits. As a rule of thumb the radiated emission TEMPEST requirements are about two orders of magnitude (40 dB) more stringent than … [Read more...]
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- …
- 41
- Next Page »