In the world of signal integrity, we rely on many important metrics to qualify high-speed channel designs, both before prototyping and during prototype testing. There is a common group of signal integrity metrics that appear in high-speed digital interface standards and which need to be implemented in printed circuit boards and packages. These signal integrity metrics … [Read more...]
Filter Installation Issues Pt. 3: Mounting and More
This article is the 3rd and final part of a three-part Filter Installation Issues series. Read Part 1: Input and Output Conductors here. Read Part 2: The Synergy of Filtering and Shielding here. There are now many suppliers of PCB-mounted shielding-cans that can be used with three-terminal filters, and they have many types that can be automatically assembled like any … [Read more...]
Reliable and Dependable Biconical Antennas 20 MHz to 18 GHz
For many years, most standards called for the use of a half-wave dipole antenna set for frequencies above 80 MHz. However, to reduce test time, broadband antennas such as the biconical antenna and log periodic antennas began to be accepted. Broadband antennas, compared to half wave dipoles, reduce test time because the technician did not have to stop the test to adjust the … [Read more...]
CubeSats: Flying Above and Within the Fray
All satellites are vulnerable to a wide variety of EMC and environmental effects, from launch to deployment. Of particular concern is the effects of Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) events. These are caused by sun activities that result in waves of cosmic rays and particles and electromagnetic energy. Significant CME events occur in sync with the “11 Year Sunspot Cycle” which, … [Read more...]
Guide to Real-Time Spectrum Analyzers: Types
Introduction The spectrum analyzer is the one “go-to” tool for every RF, microwave, and EMC/EMI engineer. In recent years, a new acquisition technology has developed, based on FFT capture and digital signal processing – the real-time (RT) spectrum analyzer. This series of articles will review the basics of conventional swept versus real-time spectrum analyzers and highlight … [Read more...]
Exodus Model AMP4025P-5KW Pulse SSPA, 3.1 – 3.5GHz, 5KW
Exodus Advanced Communications' AMP4025P-5KW operates from 3.1-3.5GHz, delivering 5KW minimum pulse power with excellent RF pulse fidelity. It features a class AB design with -20dBc harmonics and -60dBc spurious. The system includes extensive control and monitoring via a large touchscreen or remote interface, housed in a 17-inch, 8U chassis. Learn more and download the data … [Read more...]
How to Specify Board-Level Shielding
The Purpose of Board Level Shields Board level shields (BLS) are generally small metallic shielded boxes mounted directly to PC board ground return layers. There are three primary purposes of board level shields: Isolation of sensitive circuitry from other noisy circuits on the board Trapping the emissions from noisy circuits on a board from propagating to the outside … [Read more...]
Exodus AMP2074P-2KW, 1.0–2.5 GHz, 2KW Pulse Amp
Exodus Advanced Communications' AMP2074P-2KW Pulse Amp is designed for Pulse, EMC/EMI Mil-Std 461 and Pulse Radar applications. Provides Superb Pulse Fidelity up to 100usec pulse widths. Duty cycles to 10% with a minimum 63dB gain. Available monitoring parameters for Forward/Reflected power in Watts & dBm, VSWR, voltage, current, temperature sensing for outstanding … [Read more...]
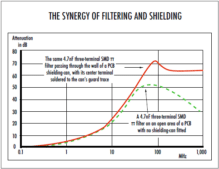
Filter Installation Issues Pt. 2: The Synergy of Filtering and Shielding
This article is part 2 of a three-part Filter Installation Issues series. Read Part 1: Input and Output Conductors here. Some mains filter manufacturers only design and specify their filters to provide attenuation over the frequency range of the conducted emissions tests (typically up to 30MHz for commercial and industrial products), to keep costs low. Unfortunately, if … [Read more...]
Space Weather – Predicting EMC Effects of Solar Storms
When we think about weather, we know what it is. We feel it, worry about it, and talk about the heat, the moisture, the wind. Weather is dynamic, though mostly predictable because we can measure its conditions. We also know that the atmosphere involves large scale electrical activity. Cloud masses move above and below each other, generating enormous static-electricity … [Read more...]